Tabla de contenido
Hello! Today we bring you more utilities for linux. Specifically we bring you the 5 administration utilities that you must have installed if or if to make the administration of your server or pc easier for you.
Let’s start:
1- lsof
The lsof utility is the software par excellence to find out which PID (process identifier) is writing to which file. It is used to know where is the log of an application to detect which process is still active writing to a process. If you use your imagination you can find thousands of everyday uses for this software.
The way to use it is:
View all the files of a PID:
lsof -p PID
root@portatil:~# lsof -p 31074
lsof: WARNING: can't stat() fuse.gvfsd-fuse file system /run/user/1000/gvfs
Output information may be incomplete.
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
bash 31074 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 6815746 /home/ger
bash 31074 root rtd DIR 253,1 4096 2 /
bash 31074 root txt REG 253,1 1113504 5636103 /bin/bash
bash 31074 root mem REG 253,1 47568 1839932 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnss_files-2.27.so
bash 31074 root mem REG 253,1 97176 1839926 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnsl-2.27.so
View all PIDs by writing to a file or directory:
root@portatil:~# lsof /var/log/syslog
lsof: WARNING: can't stat() fuse.gvfsd-fuse file system /run/user/1000/gvfs
Output information may be incomplete.
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
rsyslogd 983 syslog 7w REG 253,1 810316 5245214 /var/log/syslog
View all PIDs and files they write to:
root@portatil:~# lsof
COMMAND PID TID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
systemd 1 root cwd DIR 253,1 4096 2 /
systemd 1 root rtd DIR 253,1 4096 2 /
systemd 1 root txt REG 253,1 1595792 1839738 /lib/systemd/systemd
systemd 1 root mem REG 253,1 1700792 1839905 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libm-2.27.so
systemd 1 root mem REG 253,1 121016 1840002 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libudev.so.1.6.9
systemd 1 root mem REG 253,1 84032 1839883 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgpg-error.so.0.22.0
systemd 1 root mem REG 253,1 43304 1839894 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libjson-c.so.3.0.1
systemd 1 root mem REG 253,1 34872 2367413 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libargon2.so.0
systemd 1 root mem REG 253,1 432640 1839864 /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdevmapper.so.1.02.1
2- iptraf
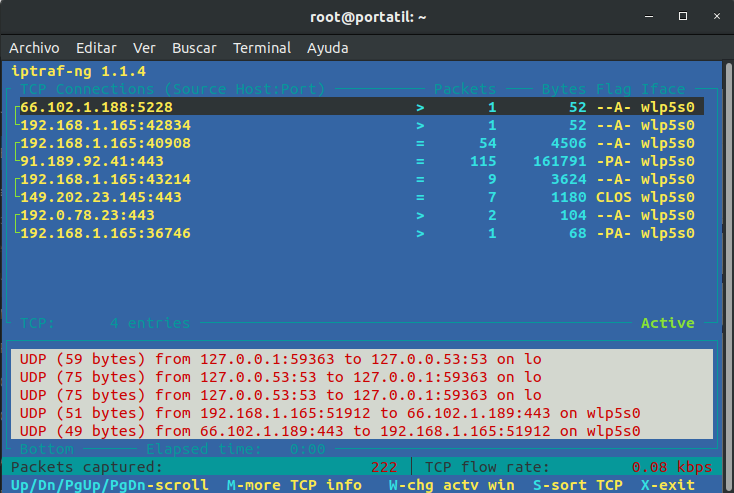
Iptraf is a network sniffer. It provides statistics on network traffic. It gives us the traffic per interface, traffic volume per IP, per MAC, etc.
Thanks to this utility you can identify from which IPs we receive traffic or to which we get it, which is the IP that consumes more network traffic and much more.
Here you have some images so you can see how it looks like:
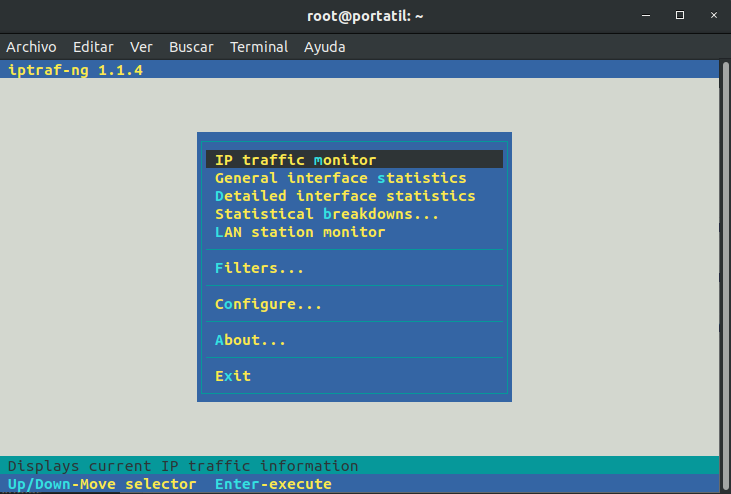
This is the main menu
Traffic from all interfaces
3- iperf
Iperf is the utility par excellence for network testing. There are several versions. The current iperf v3 is the most convenient as it incorporates many improvements over the previous one. This utility provides the network speed between a point “a” and a point “b”. You can test both TCP and UDP.
To see all the options you can run iperf –help.
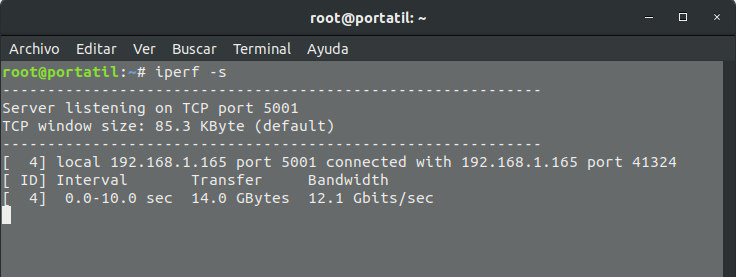
- Iperf -s” is the option that makes it run listening on a port, this option has to be at a point “a” and “b”.
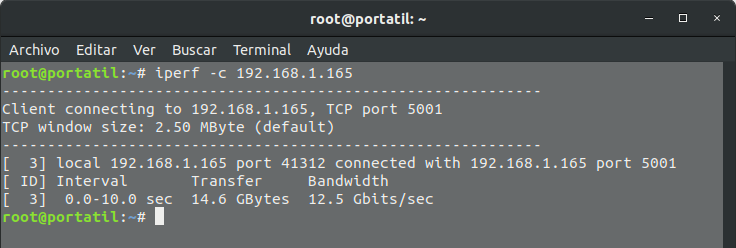
- At the other point, the client option “iperf -c XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX.XX” is executed, where the Xs indicate the server ip
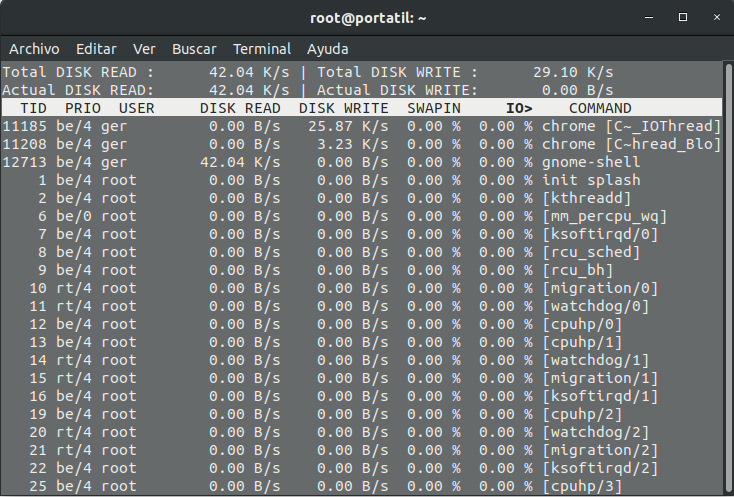
4- iotop
With this software we can see which process is writing more data flow to the disk. The way of representing the data is quite similar to a common “top”. But the difference is that the top does not represent the highest CPU and RAM usage, but the highest disk write usage.
This is an iotop image:
5- ncdu
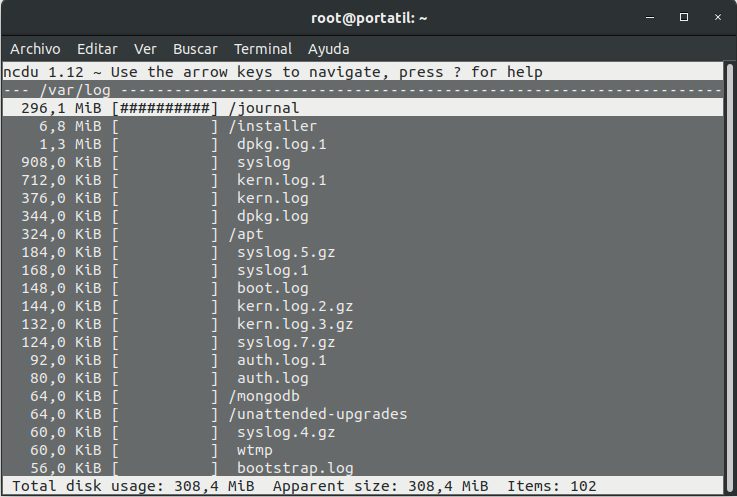
This is the best utility ever created to find out where is the cause of disk occupation. It is great not only for its simplicity of use. To use it just run “ncdu PATH_TO_CHECK” and it will return the list of directories sorted by disk occupation. It allows the navigation in the directories and sub-directories and continues ordering by occupation the content every time we access to a sub-directory.
After executing “ncdu /var/log”, then it shows the following (on my PC):
That’s all for today about the 5 admin utilities you must have installed.
If you liked it, please share it on your social networks.
See you soon!
We recommend the following books: